Patient: Peripheral Vascular Disease
In the United States, approximately 8 to 12 million patients are affected with Peripheral Vascular Disease. An estimated 600,000 interventional procedures are performed for the treatment of lower limb arterial disease each year, including Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA), bypass surgery and amputation.
Risk factors for Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) include the following:
- More than 50 years old
- History of smoking
- History of diabetes
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
- History of high blood pressure
- History of high cholesterol
- History of hyperlipidemia
- Genetic factors
The most common symptom of PVD is intermittent claudication, defined as pain on walking that is relieved by rest. Intermittent claudication accounts for 90% of all symptomatic cases of PVD, and 75% of all diagnosed cases of PVD. In PVD the femoral and/or popliteal arteries tend to be highly diffuse, with long chronic total occlusions or long segments with multiple narrowed areas.
Treatment options for PVD include conservative medical management and more aggressive invasive therapies including percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), surgical bypass, and amputation. Procedural estimates for the year 2000 identify PVD treatments as noted below:
- 70,000 Angioplasty with or without stent placement
- 150,000 Bypass surgeries
- 30,000 Limb amputations
Because vascular brachytherapy has become the standard of care for the treatment of in-stent restenosis in the coronary arteries, it is expected that vascular brachytherapy will be as successful in the treatment of PVD. The use of vascular brachytherapy in the peripheral vasculature could encourage treatment of patients with less severe disease in order to prohibit further occlusion, be effective in the treatment of patients with more severe disease who are unwilling to undergo surgery, improve treatment in angioplasty patients, and replace surgery for some patients who would otherwise have to undergo surgical bypass or amputation.
The MOBILE Trial has been developed to study the safety and effectiveness of our Strontium90-based peripheral vascular brachytherapy system, for the treatment of in-stent restenosis within the arteries of the legs. Within the MOBILE Trial, patients will be randomized to treatment with vascular brachytherapy or no additional treatment after the angioplasty procedure.
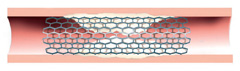
Stented artery of the leg with area of in-stent restenosis.
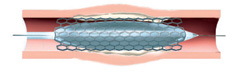
Balloon angioplasty catheter inside stented artery.
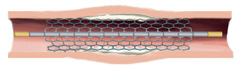
Radiation source train placed at treatment site for <5 minutes.
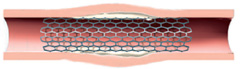
Peripheral artery post balloon angioplasty and vascular brachytherapy treatment.
For information regarding hospitals and physicians in your area that participate in the MOBILE Trial, please call 800-NOVOSTE.